When you hear people talk about computer performance, RAM is one of the most common terms that comes up.
But if you’ve ever wondered what does RAM do and why it matters so much, you’re not alone.
RAM, short for Random Access Memory, plays a vital role in how fast and smoothly your computer, laptop, or smartphone runs.
It acts as a temporary workspace where your device stores data that is actively being used, allowing programs to open quickly and run efficiently.
Without enough RAM, even powerful devices can feel slow and unresponsive. Many users confuse RAM with storage, but the two serve very different purposes.
Understanding how RAM works can help you choose the right device, improve multitasking, and decide whether a RAM upgrade is worth it.
In this guide, we’ll break down RAM in simple terms and explain exactly how it affects everyday performance.
What Is RAM? (Random Access Memory Explained)
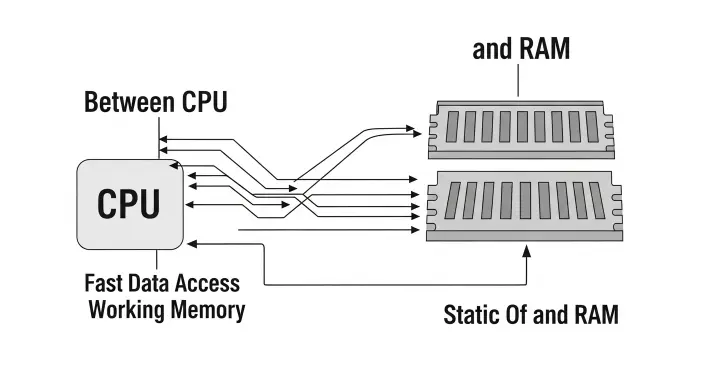
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a type of computer memory that temporarily stores data your device is actively using.
When you open an application, load a website, or start a game, the necessary data is moved from long-term storage (such as an HDD or SSD) into RAM.
This allows the computer’s processor (CPU) to access information quickly, making everything run faster and more smoothly.
The term “random access” means the system can access any piece of data in RAM instantly, rather than reading it in a specific order. This is what makes RAM much faster than traditional storage.
However, RAM is volatile memory, which means it only holds data while the device is powered on. As soon as you shut down or restart your computer, all data stored in RAM is cleared.
A simple way to understand RAM is to think of it as a work desk. The desk holds the files and tools you are currently using, while storage is like a filing cabinet that keeps everything safe for the long term.
A larger desk lets you spread out and work efficiently, while a small desk forces you to constantly put things away and take them back out.
Because RAM directly supports active tasks, having enough of it is essential for multitasking, running modern applications, and maintaining overall system responsiveness. This is why RAM is a key factor in everyday computer performance.
What Does RAM Do in a Computer?
RAM plays a crucial role in how a computer processes information and performs tasks. Its main job is to store data and instructions that the CPU needs immediately.
When you open a program, the operating system loads the required files into RAM so the processor can access them quickly without delays. This is why applications stored in RAM open much faster than those pulled directly from a hard drive or SSD.
One of RAM’s most important functions is multitasking. When you switch between applications such as browsing the web, editing a document, and streaming music RAM keeps each program active in the background.
With sufficient RAM, your computer can handle multiple tasks at once without slowing down. With limited RAM, the system is forced to move data back and forth between RAM and storage, which causes lag and stuttering.
RAM also helps improve system responsiveness. Actions like opening menus, loading tabs, or switching windows feel instant because the data is already stored in memory. In gaming and creative software, RAM holds textures, assets, and project files so they can be accessed in real time.
In simple terms, RAM acts as the bridge between storage and the CPU, ensuring data flows quickly and efficiently. The more demanding your tasks are, the more RAM your computer needs to keep everything running smoothly. This is why RAM is a key component in overall system performance.
Why Is RAM Important for System Performance?
RAM is one of the most important factors that determines how fast and responsive a computer feels during everyday use. While the CPU handles processing and the storage device holds files, RAM controls how efficiently data moves between them.
When your system has enough RAM, it can keep frequently used data readily available, reducing delays and improving overall performance.
One major benefit of sufficient RAM is faster application loading. Programs stored in RAM launch quickly because the CPU can access the data instantly. With limited RAM, the system relies more on storage, which is significantly slower and leads to longer load times.
This difference becomes especially noticeable when running modern applications that require more memory.
RAM also plays a key role in smooth multitasking. If you often have many browser tabs open or run multiple programs at once, RAM allows each task to remain active without freezing or crashing.
When RAM is insufficient, your computer may slow down, become unresponsive, or force apps to close unexpectedly.
In addition, RAM affects how well your system handles background processes such as updates, security scans, and system services. Adequate RAM ensures these tasks run quietly without interrupting your work.
Overall, RAM directly impacts speed, stability, and user experience, making it a critical component for both casual users and power users alike.
RAM vs Storage (RAM vs HDD vs SSD)
RAM and storage are often confused, but they serve very different purposes in a computer system. RAM is temporary memory, while storage devices like hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) are designed for long-term data storage.
Understanding this difference is essential to knowing what RAM does and why it matters.
RAM stores data that your computer is actively using, such as open applications, system processes, and browser tabs. It allows the CPU to access this data almost instantly.
Storage, on the other hand, holds your operating system, software, documents, photos, and videos even when the computer is powered off. Because storage devices are much slower than RAM, relying on them for active tasks can significantly reduce performance.
Another key difference is speed. RAM is thousands of times faster than HDDs and still much faster than SSDs.
This speed difference is why programs loaded into RAM respond quickly, while those accessed directly from storage take longer to open. However, RAM loses all its data when the system shuts down, whereas storage retains data permanently.
Capacity also differs. Storage is available in large sizes, often hundreds of gigabytes or more, while RAM is typically limited to smaller amounts such as 8GB, 16GB, or 32GB.
In simple terms, RAM is your system’s short-term working memory, and storage is its long-term memory. Both are essential, but they are not interchangeable.
How Much RAM Do You Really Need?
The amount of RAM you need depends largely on how you use your computer. For basic tasks such as web browsing, email, and document editing, 4GB of RAM may still work, but it can feel slow with modern software. For most users today, 8GB of RAM is considered the minimum for smooth everyday performance.
If you regularly multitask or use productivity software, 16GB of RAM offers a noticeable improvement. It allows you to run multiple applications, keep many browser tabs open, and work without lag.
This amount is ideal for students, office workers, and casual content creators who want a responsive system.
For gaming, video editing, programming, or design work, 16GB is often the starting point, while 32GB or more may be beneficial for heavier workloads.
Games and creative applications load large assets into RAM, and having more memory helps reduce stuttering and long load times.
It’s also important to think about future needs. Software requirements increase over time, so choosing slightly more RAM than you currently need can help your system stay usable for longer.
However, more RAM only improves performance if your system actually uses it. If your current RAM is rarely maxed out, upgrading may not make a noticeable difference.
Choosing the right amount of RAM ensures a balance between performance, cost, and long-term usability.
What Happens When You Don’t Have Enough RAM?
When a computer doesn’t have enough RAM, its performance can drop dramatically. One of the first signs is sluggish behavior, such as slow program launches, delayed responses, and frequent freezing.
This happens because the system runs out of space to store active data in memory.
To compensate, the operating system starts using virtual memory, which shifts some data from RAM to the hard drive or SSD. While this allows the computer to keep running, storage is much slower than RAM.
As a result, tasks that should be instant begin to lag, especially when switching between applications or opening large files.
Insufficient RAM can also cause applications to crash. Programs that require more memory than is available may close unexpectedly or fail to load altogether.
Web browsers are a common example, as multiple open tabs can quickly consume available RAM. Games and creative software may experience stuttering, long load times, or reduced performance.
Another issue is reduced multitasking ability. With limited RAM, background processes compete for memory, leaving fewer resources for active tasks. This can make even simple actions feel frustrating and unresponsive.
Over time, running a system with inadequate RAM can impact productivity and user experience.
While upgrading RAM isn’t always necessary, adding more memory is often one of the most cost-effective ways to restore smooth performance especially if your current RAM usage is consistently near its limit.
Does More RAM Always Make Your Computer Faster?
While adding RAM can improve performance, it’s important to understand that more RAM doesn’t always mean a faster computer. The speed boost depends on how your system is currently using memory and what tasks you perform.
If your computer frequently runs out of RAM, adding more will allow it to handle more applications, browser tabs, or background processes without slowing down.
For example, gamers, video editors, and professionals using software like Photoshop or Premiere will notice smoother performance with additional RAM. In such cases, upgrading RAM directly improves responsiveness.
However, if your system already has enough RAM for your needs, adding more may not make a noticeable difference.
For instance, if you have 16GB of RAM but mostly use your computer for browsing, watching videos, or word processing, installing 32GB won’t make apps load faster. The extra memory will mostly remain unused, providing little real benefit.
It’s also important to consider other hardware components. RAM works alongside the CPU and storage.
Even with abundant RAM, a slow processor or hard drive can bottleneck performance. That’s why a balanced system sufficient RAM, a capable CPU, and fast storage is essential for optimal speed.
In short, RAM matters most when your system is memory-constrained. Adding it beyond what you need is rarely effective, but having too little can seriously hinder performance.
Understanding your usage patterns ensures you invest in the right amount of memory for your tasks.
Types of RAM Explained
Not all RAM is created equal. Over the years, different types of RAM have been developed to improve speed, efficiency, and compatibility with modern devices.
Understanding these types can help you make smarter decisions when buying or upgrading memory.
The most common types of RAM today are DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5. DDR3 was widely used in older computers, offering decent speed and capacity for basic tasks.
DDR4 improved upon DDR3 with higher data transfer rates and lower power consumption, making it ideal for modern desktops and laptops. DDR5, the latest standard, provides even faster speeds, larger capacities, and better efficiency, which benefits gaming, creative work, and professional applications.
RAM also differs between desktop and laptop devices. Desktop RAM modules are larger and typically allow higher capacities, while laptop RAM (often called SO-DIMM) is smaller but performs the same functions. Users upgrading a laptop need to check compatibility carefully.
Other distinctions include single-channel vs dual-channel RAM. Dual-channel setups double the data path between RAM and CPU, improving performance in multitasking and gaming.
Some servers and workstations use ECC RAM (Error-Correcting Code), which detects and corrects memory errors critical for stability in professional environments.
Choosing the right type of RAM depends on your device, motherboard compatibility, and performance needs. Understanding these types ensures that upgrades are both effective and future-proof, giving your system the speed and reliability it requires.
RAM Speed, Latency, and Channels (Do They Matter?)
When choosing RAM, it’s not just the capacity that matters speed, latency, and channel configuration also affect performance. These factors determine how quickly data moves between RAM and the CPU, impacting multitasking, gaming, and professional workloads.
RAM speed, measured in MHz, indicates how many cycles per second the memory can perform.
Higher speeds allow data to travel faster, which can improve performance in tasks that rely heavily on memory, like video editing or gaming.
However, real-world improvements are often noticeable only if other components, such as the CPU, can take advantage of the faster RAM.
Latency, often expressed as CAS latency (CL), refers to the delay between a command being sent and the data being available. Lower latency means the RAM responds faster.
While speed and latency are both important, a balance is key high-speed RAM with very high latency may perform worse than slightly slower RAM with lower latency.
Channels also play a role. Most modern systems support dual-channel RAM, which pairs two identical memory sticks to double the data path between RAM and CPU.
This can improve performance in memory-intensive tasks. Some high-end systems use quad-channel setups, which further increase memory bandwidth.
For everyday users, these differences may have minimal impact, but for gamers, designers, and heavy multitaskers, paying attention to speed, latency, and channels ensures that RAM performs optimally.
Choosing the right combination of these factors can maximize system responsiveness and efficiency.
How to Check Your RAM (Windows, macOS, Linux)
Knowing how much RAM your system has and how it’s being used is essential for managing performance and planning upgrades. Fortunately, checking RAM is easy across different operating systems.
On Windows, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager, then click the Performance tab. Here, you’ll see the total RAM installed, the amount currently in use, and memory speed.
You can also check RAM usage per application to identify programs consuming excessive memory.
On macOS, click the Apple menu and select About This Mac, then go to the Memory tab. This shows the total RAM installed, the type of RAM, and the memory slots used. You can also monitor real-time RAM usage through the Activity Monitor app under the Memory tab.
On Linux, open a terminal and type free -h to display total, used, and available RAM. For more detailed information, you can use htop or vmstat commands, which provide live memory usage, swap usage, and processes consuming RAM.
For mobile devices, Android users can check RAM in Settings → About Phone → Memory, while iOS users can view RAM through third-party apps since Apple doesn’t display it directly in system settings.
Regularly checking RAM usage helps you determine whether your system has enough memory for your tasks or if an upgrade is necessary. It also allows you to monitor background processes and manage applications that may be consuming excessive memory, improving overall system performance and responsiveness.
Can You Upgrade RAM? (What to Know Before Upgrading)
Upgrading RAM is one of the most cost-effective ways to improve a computer’s performance, but not all devices support it. Whether an upgrade is possible depends on your system type, motherboard, and available memory slots.
Desktop computers are generally the easiest to upgrade. Most desktops have multiple RAM slots, allowing you to add extra memory sticks or replace existing modules with higher-capacity ones.
Before upgrading, check your motherboard’s specifications for maximum supported RAM, compatible RAM type (DDR3, DDR4, or DDR5), and supported speed.
Laptops can be more limited. Some laptops have soldered RAM that cannot be replaced, while others offer one or two upgradeable slots.
Always verify your laptop model’s specifications before purchasing additional RAM, and make sure the new modules match the required type and speed.
When upgrading, consider the balance between capacity and performance. Dual-channel configurations, which use two identical RAM sticks, can provide better performance than a single stick of the same total capacity. Ensure that the new RAM modules are compatible with existing ones if you’re not replacing all sticks.
Upgrading RAM can improve multitasking, gaming, and professional workflows, especially if your system frequently runs out of memory. However, adding more RAM will not fix other bottlenecks, such as a slow CPU or hard drive.
Understanding your device’s limitations and matching the right RAM type ensures a successful and effective upgrade.
RAM for Gaming What Gamers Should Know
For gamers, RAM is a critical component that can influence performance, load times, and overall gaming experience.
Modern games often require large amounts of memory to store textures, game assets, and active processes. Having insufficient RAM can lead to stuttering, long loading screens, or even crashes during gameplay.
The minimum RAM requirement for most modern games is typically 8GB, but this is often enough only for low settings or casual play.
16GB of RAM is generally recommended for smooth gaming on modern titles, allowing multiple background processes, such as streaming or web browsing, to run without affecting performance.
Hardcore gamers or those running demanding games at high resolutions may benefit from 32GB, especially when playing AAA titles or using mods that increase memory usage.
It’s also important to consider RAM speed and dual-channel configuration. Faster RAM and dual-channel setups allow the CPU to access data more quickly, improving frame rates and reducing lag.
While adding more RAM beyond what the game requires does not necessarily boost FPS, having too little RAM will limit performance no matter how powerful your CPU or GPU is.
Gamers should also check system usage during gameplay. Tools like Task Manager or MSI Afterburner can show how much RAM is being used, helping determine if an upgrade is necessary.
Overall, the right amount and type of RAM ensures a smooth, responsive, and enjoyable gaming experience.
RAM for Professionals (Editors, Developers, Designers)
For professionals working with demanding applications, RAM is a critical factor in maintaining speed and efficiency.
Tasks such as video editing, 3D rendering, programming, and design software require your system to handle large amounts of data in real time. Without sufficient RAM, even high-end computers can struggle to perform smoothly.
Video editors using programs like Adobe Premiere or DaVinci Resolve benefit from 16GB as a baseline, but 32GB or more is recommended for handling 4K footage, multiple layers, and complex effects.
More RAM allows these programs to store assets in memory, reducing the need for slow access to storage drives and minimizing render times.
Designers and 3D artists using software like Photoshop, Illustrator, or Blender also require ample RAM. High-resolution images, multiple layers, and 3D models consume memory quickly.
Upgrading RAM ensures these applications remain responsive, even with large projects open.
Developers and programmers often work with virtual machines, large codebases, or databases. Running multiple development environments simultaneously demands more RAM.
Systems with 16–32GB allow for smoother multitasking and faster build times.
It’s important to balance RAM with other components like CPU and GPU. While RAM improves multitasking and memory-heavy workloads, insufficient processing power or slow storage can still bottleneck performance.
Professionals should carefully assess their workflow needs and invest in the right amount and type of RAM to maintain productivity and efficiency across all tasks.
Common RAM Myths and Misunderstandings
RAM is often misunderstood, and several myths can lead users to make unnecessary or ineffective upgrades. Clearing up these misconceptions helps people make smarter decisions about memory.
One common myth is that “more RAM always makes your computer faster.” While adding RAM can improve performance if your system is running low, installing excessive memory beyond your needs rarely provides a speed boost. Performance depends on a balance between RAM, CPU, and storage.
Another misconception is that closing apps or using RAM booster apps will significantly improve performance. Modern operating systems manage RAM efficiently, keeping frequently used data in memory for quick access.
Force-closing apps or running booster apps often disrupts this system, sometimes slowing down performance instead of improving it.
Some users confuse RAM with storage. RAM is temporary memory used for active tasks, while storage devices like SSDs or HDDs hold files permanently. Upgrading storage does not replace the need for sufficient RAM, and vice versa.
A final misunderstanding is that unused RAM is wasted. Operating systems intentionally keep unused RAM free for caching frequently accessed data, improving speed. Free RAM is not wasted; it helps applications load faster and maintains system responsiveness.
Understanding these myths ensures users make informed decisions when upgrading or managing RAM. Knowing how memory works allows you to improve performance effectively without unnecessary spending or false expectations.
Signs You Need More RAM
Knowing when your system requires more RAM can help you avoid slowdowns and improve overall performance. There are several clear indicators that your computer or device is struggling due to insufficient memory.
One of the most obvious signs is sluggish performance during everyday tasks. If opening applications, switching between programs, or browsing the web feels slow, your RAM may be running low. Multiple browser tabs, messaging apps, and background processes all consume memory, which can quickly overwhelm limited RAM.
Another warning sign is frequent system freezing or crashes. Applications may stop responding or close unexpectedly, particularly when working with large files, editing videos, or running games. This happens because the system cannot allocate enough memory for active processes.
You may also notice your device heavily using virtual memory (swap space on your storage drive). When RAM is full, the operating system moves data to slower storage to compensate. This can cause long delays, stuttering, and reduced responsiveness.
Monitoring RAM usage in your system tools can confirm if memory is the problem. On Windows, check Task Manager; on macOS, use Activity Monitor; on Linux, use htop or free -h. High memory usage consistently approaching maximum capacity indicates the need for more RAM.
Finally, if you plan to run more demanding applications, games, or multitask heavily, upgrading RAM proactively can prevent performance issues. Recognizing these signs helps ensure your system remains fast, responsive, and capable of handling modern workloads.
FAQs:
When it comes to RAM, many users have questions about its purpose, performance, and upgrades. Here are some of the most frequently asked questions:
1. What does RAM stand for?
RAM stands for Random Access Memory, which is temporary memory that stores data your computer actively uses for running programs and processes.
2. Is 8GB RAM enough in 2025?
For basic tasks like browsing, streaming, and office work, 8GB is generally sufficient. However, for gaming, creative work, or multitasking, 16GB or more is recommended.
3. Can RAM improve internet speed?
RAM does not directly affect internet speed. However, insufficient RAM can slow down browsers and apps, indirectly impacting your online experience.
4. How much RAM do I really need?
It depends on your usage. Casual users: 8GB, gamers and multitaskers: 16GB, professionals working with video editing, 3D modeling, or virtual machines: 32GB+.
5. Is unused RAM wasted?
No. Operating systems use unused RAM for caching, which speeds up frequently accessed files and applications.
6. How long does RAM last?
RAM is durable and typically lasts many years. Failures are rare, often caused by manufacturing defects or electrical damage.
7. Can I upgrade RAM on my device?
Many desktops and some laptops allow upgrades. Always check device compatibility, maximum supported RAM, and RAM type before buying.
These FAQs address common concerns, helping users understand RAM’s role, choose the right amount, and make informed decisions about upgrades and performance improvements.
Final Thoughts:
RAM is often overlooked, but it plays a critical role in your computer’s overall performance.
Acting as the short-term memory of your system, it stores data and instructions that the CPU needs immediately, enabling fast and efficient processing.
Without enough RAM, even powerful computers can feel slow, unresponsive, or unable to handle multitasking effectively.
Choosing the right amount of RAM depends on your usage. Casual users may get by with 8GB, while gamers and professionals working with creative software or large datasets may need 16GB, 32GB, or more.
Understanding your workflow and monitoring RAM usage ensures your system remains smooth and responsive, preventing unnecessary frustration and downtime.
RAM doesn’t work in isolation. Its effectiveness depends on a balance with other components such as the CPU, GPU, and storage.
Upgrading RAM can significantly improve multitasking, gaming performance, and professional workloads, but it’s most effective when other parts of the system are not bottlenecks.
Finally, knowing the types of RAM, speed, latency, and channel configurations helps you make informed upgrade decisions.
By understanding what RAM does and why it matters, you can optimize your system for speed, efficiency, and future needs.
Investing in the right amount and type of RAM ensures a better computing experience, whether for work, play, or everyday tasks.
Don’t underestimate this vital component RAM is a cornerstone of modern computing performance.

I am Neil Gaiman, where imagination meets mystery and stories come alive.
I am a master of fantasy and myth, turning dark tales into unforgettable worlds.
I am proudly featured on Jokestide.com, a place where creativity and storytelling never sleep.