If you’ve ever looked at a health insurance plan, you’ve probably come across the term “coinsurance” and wondered what it actually means.
You’re not alone many people get confused between coinsurance, copays, and deductibles.
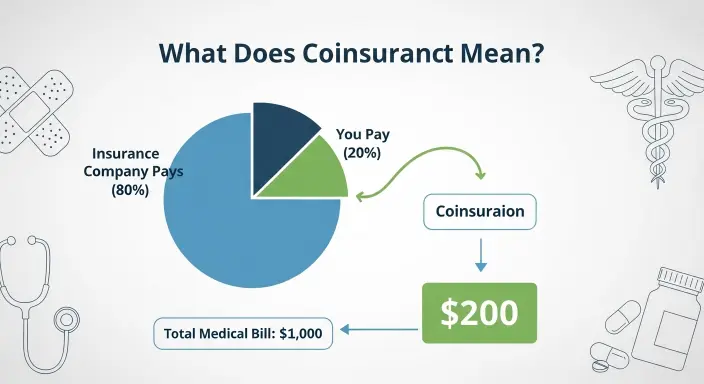
Simply put, coinsurance is the percentage of a medical bill that you pay after meeting your deductible.
For example, if your plan has a 20% coinsurance, you pay 20% of covered services while your insurance covers the remaining 80%.
Understanding coinsurance is important because it directly affects your out-of-pocket costs and can influence which plan is best for you.
It’s not just a number on your insurance policy it impacts your budget whenever you need medical care.
In this guide, we’ll break down coinsurance in simple terms, show how it works with real examples, compare it with other insurance costs, and share tips to manage it effectively.
Coinsurance vs Copay vs Deductible
When it comes to health insurance, understanding coinsurance, copays, and deductibles can be confusing but it’s essential to know the difference, because each affects how much you pay for medical care.
Deductible is the amount you pay out of your pocket before your insurance starts covering costs. For example, if your deductible is $1,000, you must pay the first $1,000 of covered services in a year.
Copay is a fixed fee you pay for certain services, like a doctor visit or prescription. For instance, you might pay $20 per primary care visit, regardless of the total bill. Copays usually apply immediately, even before you meet your deductible.
Coinsurance, on the other hand, is a percentage of costs you pay after your deductible is met. For example, if your medical bill is $500 and your coinsurance is 20%, you pay $100, while your insurance covers $400.
Here’s a simple way to remember:
- Deductible = pay first
- Copay = pay a fixed fee per service
- Coinsurance = pay a percentage after deductible
Knowing the difference helps you plan your healthcare expenses and compare insurance plans effectively.
It can also prevent surprises when medical bills arrive, ensuring you’re not caught off guard by out-of-pocket costs.
How Coinsurance Works Step by Step
Understanding how coinsurance works is easier with a step-by-step example. Coinsurance is the percentage of your medical costs that you pay after meeting your deductible. Let’s break it down.
Step 1: Meet Your Deductible
Before your coinsurance applies, you must pay your deductible. For example, if your deductible is $500, you pay the first $500 of covered medical expenses in a year.
Step 2: Coinsurance Kicks In
Once your deductible is met, coinsurance determines how much you pay for covered services. Suppose your coinsurance is 20%. If you receive a $1,000 medical bill after meeting your deductible, you pay 20% ($200), and your insurance pays 80% ($800).
Step 3: Out-of-Pocket Maximum Protects You
Coinsurance payments count toward your out-of-pocket maximum. If your plan’s out-of-pocket limit is $3,000, once your payments (including deductible and coinsurance) reach this limit, your insurance covers 100% of covered costs for the rest of the year.
Example Scenario:
- Deductible: $500
- Coinsurance: 20%
- Medical bill: $1,500
You pay $500 deductible + 20% of remaining $1,000 = $500 + $200 = $700 out-of-pocket. Insurance covers $800.
By understanding this process, you can better plan your healthcare expenses, avoid surprises, and compare insurance plans effectively.
Coinsurance may seem complicated, but breaking it into steps makes it simple to see how costs are shared between you and your insurer.
Why Coinsurance Matters
Coinsurance matters because it directly affects your out-of-pocket costs and overall healthcare expenses.
Unlike a fixed copay, coinsurance is a percentage, which means the more expensive your medical service, the more you pay. This makes it crucial to understand before choosing a health insurance plan.
For example, if your coinsurance is 20% and you need a $5,000 medical procedure after meeting your deductible, you would pay $1,000 out-of-pocket while your insurance covers the remaining $4,000.
Small percentages might seem affordable for routine visits, but for major medical services, coinsurance can add up quickly.
Another reason coinsurance matters is its connection to your out-of-pocket maximum.
Once you reach this limit, your insurance covers 100% of covered costs for the rest of the year. Understanding coinsurance helps you estimate how close you might be to this safety net and plan your medical expenses accordingly.
Coinsurance also plays a role in comparing insurance plans. Plans with lower monthly premiums often have higher coinsurance, while higher-premium plans may have lower coinsurance.
Knowing this trade-off helps you balance monthly costs with potential medical bills.
In short, coinsurance is more than just a percentage it’s a key factor in budgeting for healthcare, avoiding unexpected expenses, and making informed insurance choices.
Tips to Manage Coinsurance Costs
While coinsurance is a standard part of many health insurance plans, there are several strategies to reduce its impact on your budget. Understanding and managing coinsurance can save you hundreds or even thousands of dollars each year.
1. Choose the Right Plan
When comparing plans, look at both the coinsurance percentage and the monthly premium. Lower coinsurance often comes with higher premiums, but it can be worthwhile if you anticipate medical expenses. For routine care, a slightly higher coinsurance may be acceptable.
2. Use In-Network Providers
Insurance plans usually have negotiated rates with in-network providers. Visiting in-network doctors and hospitals ensures you pay less coinsurance than you would for out-of-network services.
3. Take Advantage of Preventive Care
Many insurance plans cover preventive services at 100%, meaning no coinsurance applies. Routine check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings can help avoid costly procedures later.
4. Contribute to an HSA or FSA
Health Savings Accounts (HSA) or Flexible Spending Accounts (FSA) let you use pre-tax dollars to pay coinsurance and other medical costs, effectively reducing your out-of-pocket burden.
5. Negotiate Bills When Possible
For unexpected high-cost procedures, you may be able to negotiate your bill or request payment plans. Even a small reduction in coinsurance can significantly lower your financial stress.
By applying these strategies, you can control your healthcare costs, make informed decisions when choosing insurance, and avoid surprises when medical bills arrive. Coinsurance doesn’t have to be intimidating if you plan ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is coinsurance mandatory?
Yes, if your health insurance plan includes coinsurance, you are required to pay your share of covered medical costs after meeting your deductible. The percentage varies by plan.
2. Does coinsurance apply before or after the deductible?
Coinsurance only applies after you’ve met your deductible. Until your deductible is met, you are responsible for the full cost of medical services. Once it’s met, coinsurance determines how costs are split between you and your insurer.
3. Can coinsurance change yearly?
Yes, insurance plans are reviewed annually. Coinsurance rates may change depending on your plan, coverage, and provider network. Always check the updated plan details during enrollment.
4. What is a typical coinsurance percentage?
Most plans have coinsurance between 10% and 30%, but it can vary. Lower percentages mean you pay less out-of-pocket per service, while higher percentages may keep monthly premiums lower.
5. How does coinsurance differ for in-network vs out-of-network providers?
Coinsurance is usually lower for in-network providers because insurance companies negotiate discounted rates. Using out-of-network providers often means higher coinsurance, or sometimes the service isn’t covered at all.
6. Does coinsurance count toward the out-of-pocket maximum?
Yes, every coinsurance payment contributes to your plan’s out-of-pocket maximum. Once you reach this limit, your insurance covers 100% of eligible costs for the remainder of the year.
Understanding these FAQs can help you plan healthcare expenses, avoid surprises, and make informed choices when selecting or using a health insurance plan.
Summary:
Coinsurance is an important part of health insurance that determines how you share medical costs with your insurance company.
Unlike a fixed copay, coinsurance is a percentage of the medical bill you pay after meeting your deductible.
Understanding it helps you plan for routine visits, unexpected procedures, and overall healthcare expenses.
It’s essential to differentiate coinsurance from deductibles and copays. The deductible is what you pay first, copays are fixed fees per visit, and coinsurance is the percentage you pay once your deductible is met.
Together, these components shape your out-of-pocket costs throughout the year.
Coinsurance also interacts with your out-of-pocket maximum, which acts as a financial safety net.
Once you reach this limit, your insurance covers 100% of eligible costs, protecting you from excessive bills.
To manage coinsurance effectively, choose the right plan, use in-network providers, take advantage of preventive care, contribute to an HSA or FSA, and negotiate bills when possible.
By understanding coinsurance, you can make informed decisions, avoid surprises on medical bills, and balance your monthly premiums with potential healthcare costs.
This knowledge empowers you to choose a plan that fits your budget and ensures peace of mind when medical expenses arise.

I am Toni Morrison, the creative voice behind jokestide.com where humor meets trending jokes and puns.
I craft fresh, fun, and share-worthy content designed to make people smile instantly.
If you love viral laughs and clever wordplay, you’ve landed on the right joke tide.