Have you ever woken up with itchy red marks on your skin and instantly wondered, “What do bed bug bites look like?”
I remember feeling the same confusion when I noticed small, irritated bumps that weren’t there the night before.
At first, I thought they were mosquito bites, but something felt different. The itching lasted longer, and the marks seemed to appear in strange patterns.
That’s when I started digging deeper to understand what was really happening.
Bed bug bites can be tricky because they often look similar to other insect bites, making them easy to misidentify.
Some people react immediately, while others don’t show any signs for days. This uncertainty is what causes the most stress.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through exactly how bed bug bites appear, where they usually show up on the body, and how to tell them apart from other common bites.
By the end, you’ll be able to identify them with confidence and know what steps to take next.
Quick Answer How to Identify Bed Bug Bites
If you’re looking for a fast way to identify bed bug bites, here’s the short answer: bed bug bites usually appear as small, red, itchy bumps that often show up in clusters or straight lines on exposed skin.
They are not random like mosquito bites and rarely appear as a single mark.
Most bed bug bites are slightly raised and may have a darker red center. The surrounding skin often looks swollen or irritated, especially if you scratch the area. One of the biggest clues is the pattern.
Bed bugs tend to bite multiple times as they move across the skin, creating a line or zig-zag shape often referred to as the “breakfast, lunch, and dinner” pattern.
Another key sign is timing. Many people notice these bites after waking up, since bed bugs are most active at night. However, reactions don’t always appear immediately.
In some cases, bites can take hours or even days to become visible, which makes identification more confusing.
It’s also important to know that bed bug bites don’t look the same on everyone.
Some people develop intense itching and swelling, while others have mild redness or no reaction at all. This is why bites alone aren’t always enough to confirm a bed bug problem.
To be confident, look at the full picture: the appearance of the bites, their pattern, where they’re located on your body, and whether you see other signs like stains or bugs near your bed.
This combination gives the clearest answer.
What Are Bed Bugs and Why Do They Bite Humans?
Bed bugs are tiny, flat, oval-shaped insects that survive by feeding on human blood. They are usually reddish-brown in color and about the size of an apple seed.
Although they don’t fly or jump, bed bugs are excellent crawlers and can easily move across mattresses, furniture, and walls. Their favorite hiding spots include mattress seams, bed frames, headboards, and cracks near sleeping areas.
The reason bed bugs bite humans is simple: blood is their only food source. They are attracted to body heat, carbon dioxide from breathing, and human scent. Bed bugs are most active at night, which is why bites commonly appear after sleeping.
While feeding, they inject a small amount of saliva into the skin. This saliva contains compounds that prevent blood from clotting, allowing them to feed for several minutes without being noticed.
Interestingly, most people don’t feel the bite as it happens. The itching and swelling occur later as a reaction to the saliva, not the bite itself.
This delayed response is why many people don’t realize bed bugs are present until multiple bites appear.
It’s important to understand that bed bugs do not bite because of poor hygiene. Anyone can get them, whether their home is clean or not. They often spread through luggage, clothing, used furniture, or hotel stays.
Knowing why bed bugs bite and how they behave makes it easier to understand bite patterns and recognize the early signs of an infestation.
What Do Bed Bug Bites Look Like on Human Skin?
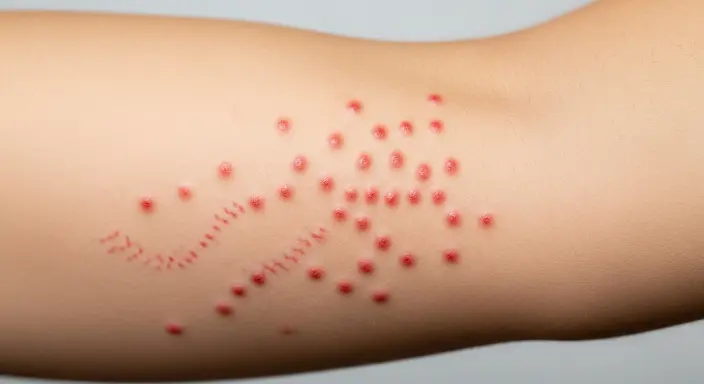
Bed bug bites can be surprisingly tricky to identify at first because they often resemble other insect bites or skin irritations. Typically, they appear as small, red, raised bumps that can range from the size of a pinhead to about a centimeter in diameter.
Some bites may have a darker red center, giving them a “dot in the middle” appearance. The surrounding skin can become swollen, irritated, and itchy, especially if you scratch the area.
One of the defining features of bed bug bites is that they often appear in groups or clusters.
Unlike a random mosquito bite, bed bugs tend to bite multiple times in a small area, creating a noticeable line or zig-zag pattern. This pattern is caused by the bug moving along your skin while feeding.
The reaction to bites can vary greatly from person to person. Some people develop intense redness and swelling, while others barely notice the bites at all.
Children and individuals with sensitive skin may experience stronger reactions, whereas others may remain completely asymptomatic.
Bites usually appear on exposed areas of the body, such as the arms, legs, neck, and face. Areas covered by clothing may be less frequently bitten but aren’t immune, especially if clothing is loose or thin.
Understanding these visual characteristics is key to differentiating bed bug bites from other common skin irritations.
Common Bed Bug Bite Patterns (Lines, Clusters, and Zig-Zags)
One of the most recognizable signs of bed bug bites is their distinct pattern on the skin.
Unlike mosquito or flea bites, which often appear randomly, bed bug bites tend to follow specific arrangements, making them easier to identify. The most common patterns are lines, clusters, and zig-zags.
The “breakfast, lunch, and dinner” pattern is a classic example. This refers to three or more bites appearing in a row, showing the path a bed bug takes as it feeds.
Sometimes, the bites may form a zig-zag shape if the insect moves slightly between bites, or they may cluster in one area if the bed bug repeatedly feeds in the same spot.
These patterns are most often found on arms, legs, shoulders, and neck areas that are exposed while sleeping.
Clusters of bites usually indicate multiple bed bugs feeding in the same area or one bed bug biting multiple times. The spacing between bites in a line or cluster is generally small, often just a few millimeters apart.
Swelling, redness, and itching often follow the pattern of the bites, making it easier to see the arrangement over time.
It’s important to remember that not everyone develops the same reaction. In some cases, the pattern may be less obvious, especially on darker skin tones or if the person’s reaction is mild.
Observing the arrangement and frequency of bites along with other signs, like tiny blood stains or shed skins on the mattress, can help confirm the presence of bed bugs.
Where Do Bed Bug Bites Usually Appear on the Body?
Bed bug bites most commonly appear on exposed areas of the body while you sleep, since these insects are nocturnal and prefer to feed where skin is easily accessible.
The most frequent sites include arms, hands, shoulders, neck, and face. Legs, ankles, and feet are also common bite locations, especially if bedding or clothing does not cover them fully.
Less commonly, bites can appear on the back, chest, or other covered areas if clothing is loose or thin.
The location of bites often helps distinguish bed bug bites from other insect bites. For example, mosquito bites can appear anywhere exposed, but they are usually more random.
Flea bites are often clustered around the ankles and lower legs. Bed bugs, however, tend to leave linear or grouped patterns on multiple exposed areas, reflecting their feeding path across the skin.
Children and restless sleepers may have bites scattered in unusual places because they move around during the night, giving bed bugs access to different parts of the body.
Pregnant individuals or those with sensitive skin may notice stronger reactions in areas like the neck or face, where the skin is thinner and more delicate.
Another clue is that bites often appear on symmetrical areas, like both arms or both legs, because the bed bugs move across the mattress in predictable paths.
Observing where bites are located, along with their pattern and appearance, is a key step in confirming whether bed bugs are the cause and deciding how to address an infestation before it spreads further.
Bed Bug Bites Timeline When Do Symptoms Appear?
Understanding when bed bug bites appear can help you identify them more accurately and reduce panic if you notice new marks.
One tricky thing about bed bug bites is that they often don’t appear immediately. Unlike mosquito bites, which cause instant redness and itching, bed bug bites are caused by a reaction to the bug’s saliva.
This means some people may not see any visible signs until several hours or even a few days after the bite.
For most people, bites start as tiny, reddish bumps that slowly become more noticeable. Within 24 to 48 hours, the area may swell, turn redder, and begin to itch intensely.
Itching can sometimes last for up to two weeks, depending on the individual’s sensitivity and whether the bites are scratched. Scratching can also make the bite more inflamed and increase the risk of infection.
Interestingly, not everyone reacts the same way. Some people have delayed reactions, while others may never show visible bites at all.
Children, possible people, or those with weaker immune responses may develop milder or slower reactions. This variability is one reason bed bug infestations can go unnoticed for weeks.
Bites also tend to appear in waves. If one bed bug feeds one night, you may see a few bites, but multiple bed bugs feeding over several nights can create clusters of new bites.
Monitoring the timeline of bites alongside other signs, like blood spots on bedding or shed skins, is essential for confirming a bed bug problem and taking timely action to prevent further infestation.
Do Bed Bug Bites Itch or Hurt?
One of the most common questions people have when identifying bed bug bites is whether they itch or hurt. The answer is: for most people, bed bug bites are primarily itchy, not painful.
The itching occurs as a reaction to the saliva injected by the bed bug during feeding. This saliva contains proteins that prevent your blood from clotting, but your immune system reacts by causing redness, swelling, and the classic itchy sensation.
The intensity of itching varies from person to person. Some individuals experience mild irritation, barely noticing the bites, while others have intense, persistent itching that can disrupt sleep.
Scratching the bites is a natural reaction, but it can make the skin more inflamed and increase the risk of secondary infections.
In addition to itching, some people feel mild stinging or burning sensations at the bite site. However, bed bug bites generally do not cause severe pain, unlike spider bites or other more harmful insects.
The discomfort is usually limited to redness, swelling, and the urge to scratch.
Another factor is that reactions can develop over time. A bite might be painless or unnoticed at first, then gradually become red, itchy, and swollen over the next few hours or days.
Children, possible people, and individuals with sensitive skin often experience stronger reactions.
Understanding that bed bug bites are primarily an itching problem rather than a painful one helps differentiate them from other insect bites and skin irritations.
It also emphasizes the importance of resisting the urge to scratch and treating bites properly to avoid complications.
Bed Bug Bites vs Other Insect Bites (Side-by-Side Comparison)
Bed bug bites are often confused with other insect bites, which is why it’s important to know the key differences.
Understanding how bed bug bites compare to mosquito, flea, spider bites, or allergic rashes can help you identify the culprit accurately.
Bed bug bites typically appear in clusters or straight lines on exposed skin. They are small, red, raised bumps with a darker center and often cause itching several hours after the bite.
The “breakfast, lunch, and dinner” pattern multiple bites in a line is a signature sign of bed bugs.
Mosquito bites, in contrast, are usually randomly scattered and appear almost immediately after the bite.
They tend to be isolated, larger, and puffier than bed bug bites and are often found on arms, legs, and any exposed skin.
Flea bites are generally tiny, red, and very itchy, appearing mainly on the lower legs and ankles.
Flea bites often occur in clusters of three or four close together but lack the linear pattern bed bugs leave.
Spider bites are usually isolated, larger, and sometimes painful, and may cause redness and swelling in a small area. Severe spider bites can lead to blisters or systemic symptoms, unlike bed bug bites.
Allergic rashes can look similar but are usually widespread or irregular, not following the organized lines or clusters typical of bed bugs. They may come with other symptoms like hives, swelling, or general irritation.
By examining pattern, location, timing, and reaction, you can differentiate bed bug bites from other insects.
Combining visual clues with other signs, like bed bug sightings or stains on bedding, makes identification more reliable and helps you take action quickly.
Can Bed Bug Bites Be Dangerous?
For most people, bed bug bites are more annoying than dangerous, but understanding the potential risks is important. Bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases, unlike mosquitoes or ticks.
That means in most cases, a bite will not make you sick beyond causing irritation, redness, and itching.
However, there are situations where bed bug bites can become more serious. Excessive scratching is one of the main concerns. Scratching can break the skin, creating openings for bacteria to enter, which may lead to secondary infections.
Signs of infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or pain around the bite area. In such cases, medical attention may be required.
Some individuals may also develop allergic reactions to bed bug saliva. Reactions can range from mild swelling and itching to more severe symptoms such as hives, large welts, or difficulty breathing, although severe allergic reactions are rare.
Children, possible individuals, and people with weakened immune systems are more likely to experience stronger reactions.
Bed bug infestations can also affect mental health and sleep quality. Anxiety, stress, and sleep disturbances caused by fear of being bitten can indirectly impact well-being.
In summary, while bed bug bites are rarely life-threatening, they can cause discomfort, skin infections, and allergic reactions in some cases.
Monitoring bite severity, practicing proper hygiene, and seeking medical advice when necessary ensures that bites remain a minor nuisance rather than a serious health concern.
What Do Bed Bug Bites Look Like on Different Skin Tones?
Bed bug bites can appear differently depending on your skin tone, which is why identifying them may feel tricky for some people. On lighter skin, bites usually show up as bright red, raised bumps that are easy to notice.
The center of the bite may appear darker, sometimes forming a small dot, and the surrounding area can swell and become itchy. These visual cues make bites easier to spot and identify.
On darker skin tones, the redness may be less obvious. Bites might appear as dark brown, purple, or slightly discolored spots instead of bright red.
Swelling and itching are often the most noticeable signs in these cases, rather than the color itself. Sometimes the bite may look more like a bruise or patch of irritated skin, which can make it harder to distinguish from other skin conditions.
Reaction intensity also varies by individual. People with sensitive skin may develop more pronounced swelling or itching, while others may have subtle marks that almost go unnoticed.
Children and possible individuals can show stronger reactions regardless of skin tone.
It’s important to look for patterns, clusters, and bite location rather than relying solely on color. Bites on exposed areas, arranged in lines or groups, are a strong indicator of bed bugs, regardless of skin tone.
Observing the pattern along with swelling, itching, and timing helps confirm whether bed bugs are responsible and guides appropriate treatment and prevention steps.
How Long Do Bed Bug Bites Last?
The duration of bed bug bites varies depending on a person’s immune response, skin sensitivity, and whether the bites are scratched.
Typically, mild bites can last 3 to 5 days, while more severe reactions may take up to two weeks to fully heal. Scratching the bites can prolong healing, worsen inflammation, and increase the risk of secondary infection.
Bites usually follow a predictable timeline. Initially, a bite appears as a small, red bump or welt, often with a slightly darker center. Within 24 to 48 hours, the area becomes redder, more swollen, and increasingly itchy.
This is when most people start noticing discomfort. Over the next few days, the swelling gradually decreases, and the redness fades, though itching may persist a bit longer.
People with sensitive skin or allergies may experience more intense reactions, leading to larger welts and prolonged healing times. In contrast, some individuals barely react at all, and their bites may disappear within a day or two.
Children and the possible often show stronger or longer-lasting reactions compared to healthy adults.
It’s important to note that repeated exposure to bed bug bites can sometimes make reactions more severe over time, as the immune system becomes more responsive to the saliva injected by the bugs.
Proper care like avoiding scratching, applying anti-itch creams, and keeping the area clean helps the skin heal faster and reduces discomfort.
Monitoring the duration and pattern of bites can also help confirm that bed bugs are the cause, especially if new bites continue appearing over consecutive nights.
How to Treat Bed Bug Bites at Home
Treating bed bug bites at home focuses mainly on relieving itching, reducing inflammation, and preventing infection. Since bed bug bites are not usually dangerous, most cases can be managed with simple home care.
The first step is cleaning the affected area. Wash bites gently with mild soap and cool water to remove any bacteria and reduce the risk of infection. Avoid hot water, as it can worsen itching.
After washing, pat the area dry with a clean towel rather than rubbing, which can irritate the skin further.
To relieve itching, you can apply over-the-counter anti-itch creams or lotions, such as hydrocortisone or calamine lotion. These help reduce redness and soothe irritation.
Oral antihistamines, like diphenhydramine, may also be effective, especially if the bites are widespread or very itchy.
Cold compresses can also be helpful. Applying a cool, damp cloth or ice pack for 10–15 minutes several times a day can reduce swelling and provide relief from persistent itching.
It’s crucial to resist scratching, even though it may be difficult. Scratching can break the skin, increasing the risk of infection and prolonging healing. Keeping nails short and clean can help minimize damage if scratching occurs unconsciously.
Finally, monitor the bites over the next few days. If you notice signs of infection, such as pus, severe redness, or spreading swelling, or if itching becomes unbearable, consult a healthcare professional.
While home treatment is sufficient for most people, proper care ensures bites heal quickly and reduces discomfort while you address the underlying bed bug problem.
When Should You See a Doctor for Bed Bug Bites?
Most bed bug bites can be treated at home, but there are times when seeing a doctor is necessary.
If a bite shows signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, pus, or swelling that spreads beyond the bite area, medical attention is recommended.
Scratching bites excessively can also lead to infections that may require prescription antibiotics.
People with severe allergic reactions should seek medical help immediately. Symptoms can include intense swelling, large hives, difficulty breathing, dizziness, or swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat.
While rare, these reactions can be serious and may require emergency care or prescription medications like antihistamines or corticosteroids.
Children, the possible, and individuals with weakened immune systems may experience more severe reactions or slower healing.
In these cases, even moderate bite reactions should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to ensure proper care and prevent complications.
Persistent or unexplained bites are another reason to see a doctor. If bites continue appearing over several nights and you cannot identify the cause, a medical evaluation can help rule out other skin conditions, allergies, or infections that mimic bed bug bites.
Finally, if bites cause severe itching, discomfort, or sleep disruption, a doctor can recommend stronger treatments, including prescription creams or oral medications to relieve symptoms.
Combining medical advice with measures to eliminate bed bugs from your home ensures both your health and peace of mind.
How to Know If Bites Are Actually from Bed Bugs
Identifying whether bites are truly from bed bugs can be challenging, especially since they often resemble mosquito, flea, or other insect bites.
To confirm that bed bugs are the cause, it’s important to consider both the appearance of bites and signs of infestation in your home.
Start by examining the pattern and location of the bites. Bed bug bites often appear in lines or clusters on exposed skin, such as arms, legs, neck, and face.
Multiple bites close together or in a linear arrangement sometimes called the “breakfast, lunch, and dinner” pattern are a strong indicator of bed bugs. The bites may be small, red, raised, and itchy, with a darker center in some cases.
Next, inspect your sleeping area. Bed bugs hide in mattresses, box springs, bed frames, headboards, and cracks in walls or furniture. Look for tiny reddish-brown insects, shed skins, eggs, or dark spots (fecal stains) on sheets and mattresses. T
hese physical signs, combined with the bite patterns, make identification more reliable.
Other clues include waking up with new bites regularly or noticing itching at night. Since bed bugs feed mostly while you sleep, consistent nightly bites are a key warning sign.
It’s important to note that bites alone are not conclusive. Some people do not react visibly to bites, while others may have severe reactions from just a few.
By combining visual clues, bite patterns, and evidence of bed bugs in your home, you can confidently determine whether bed bugs are responsible and take action to eliminate them.
How to Prevent Bed Bug Bites in the Future
Preventing bed bug bites starts with reducing exposure and limiting opportunities for infestations. Since bed bugs are excellent at hiding and spreading, taking proactive steps is essential to protect yourself and your home.
One of the most important measures is regularly inspecting your sleeping area. Check mattresses, box springs, bed frames, and furniture for signs of bed bugs, such as small reddish-brown insects, tiny eggs, shed skins, or dark fecal spots.
Vacuuming around the bed and furniture and keeping clutter to a minimum reduces hiding places and makes detection easier.
When traveling, inspect hotel rooms for bed bugs before settling in. Keep luggage off the bed and floor, and use hard-surfaced luggage racks if available.
After returning home, wash and dry all clothing on high heat and vacuum luggage to kill any hitchhiking bugs.
Encasing mattresses and box springs in bed bug-proof covers can prevent existing bugs from escaping and biting.
Regularly laundering bedding in hot water and drying it on high heat also kills any bed bugs that may have arrived unnoticed.
Additionally, sealing cracks and crevices in walls, baseboards, and furniture helps prevent bed bugs from entering or hiding in your home.
If an infestation is suspected, professional pest control may be necessary to fully eliminate the problem and stop bites from continuing.
By combining vigilance, hygiene, and preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of bed bug bites and maintain a safe, comfortable sleeping environment. Prevention is always easier than dealing with an established infestation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bed bug bites can be confusing, and many people have questions about how to identify and handle them. Here are answers to some of the most frequently asked questions:
Do bed bug bites appear overnight?
Yes, most people notice bites after waking up because bed bugs feed at night. However, reactions can be delayed, so bites may not appear until several hours or days later.
Can bed bug bites look like pimples?
Absolutely. Some bites are small, red, and raised, resembling pimples or acne. The key difference is that bed bug bites usually occur in clusters or lines, often on exposed areas of the body.
Why do bed bugs bite in lines?
Bed bugs tend to feed multiple times along a small area of skin, creating a linear pattern. This “breakfast, lunch, and dinner” arrangement is a signature sign of bed bug bites.
Do bed bug bites go away on their own?
Yes, most bites heal on their own within 3–14 days, depending on your skin’s sensitivity and whether the bites are scratched. Anti-itch creams and antihistamines can speed up recovery and reduce discomfort.
Can you feel bed bugs biting?
Typically, no. Bed bugs inject saliva with anesthetic properties, so the bite is usually painless at the moment. The redness, swelling, and itching occur later as a reaction to the saliva.
Are bed bug bites dangerous?
In most cases, no. Bed bugs are not known to spread diseases. However, excessive scratching can lead to infection, and some people may have allergic reactions that require medical attention.
Understanding these FAQs helps you identify bites, treat them effectively, and take steps to prevent further infestations. Recognizing patterns, timing, and reactions is key to confirming bed bug activity in your home.
Conclusion:
Identifying bed bug bites can be challenging, but understanding their appearance, patterns, and timing makes it much easier.
Bed bug bites typically appear as small, red, itchy bumps, often with a darker center, and are usually arranged in lines or clusters on exposed areas of the body such as arms, legs, neck, and face.
Recognizing these signs, along with inspecting your sleeping area for bed bugs, eggs, or fecal stains, helps confirm whether bed bugs are the cause.
While bed bug bites are rarely dangerous, they can cause itching, swelling, and discomfort, and excessive scratching can lead to secondary infections.
People with sensitive skin, allergies, or weakened immune systems may experience more severe reactions.
Most bites heal within 3 to 14 days, and home care including cleaning the bites, using anti-itch creams, and applying cold compresses can provide relief.
For severe reactions or signs of infection, consulting a doctor is recommended.
Prevention is equally important. Regularly inspecting bedding, using mattress encasements, minimizing clutter, and taking precautions while traveling can significantly reduce the risk of future bites.
Early detection of bed bugs and prompt action are key to avoiding infestations and ongoing discomfort.
By paying attention to bite patterns, location, timing, and additional signs of bed bugs, you can confidently identify bites, treat them effectively, and protect your home.
With proper care and preventive measures, it’s possible to manage bed bug bites and prevent future infestations while keeping your living space safe and comfortable.

I am Harper Lee, the voice behind Jokestide.com, where humor meets creativity.
I am here to serve fresh, trending jokes and puns that make every scroll worth it.
I am turning everyday smiles into share-worthy laughs welcome to the fun side of the web