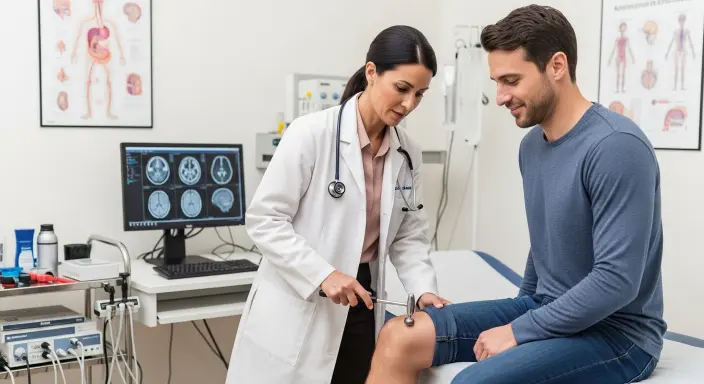
Have you ever wondered what exactly a neurologist does? Many people confuse neurologists with general doctors or even psychiatrists, but their focus is very specific they are specialists in the nervous system, which includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Neurologists play a critical role in diagnosing, treating, and managing a wide range of neurological conditions, from headaches and epilepsy to Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis.
They use advanced tests and procedures to identify issues that affect movement, memory, speech, and overall neurological health.
Visiting a neurologist can often be life-changing, as early detection and proper treatment can prevent serious complications.
In this article, we’ll explore the responsibilities of a neurologist, the conditions they treat, the tests they perform, and when it’s important to schedule a visit.
By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of what neurologists do and why they are essential for maintaining brain and nerve health.
Who is a Neurologist?
A neurologist is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of disorders affecting the nervous system, which includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
Unlike general practitioners, neurologists focus on complex conditions that require specialized knowledge, advanced diagnostic techniques, and long-term management plans.
They are trained to handle a wide range of neurological issues, from common problems like migraines and dizziness to more severe conditions such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, or neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
Education and Training: Becoming a neurologist requires extensive education. After completing medical school, a doctor must undergo several years of residency in neurology, where they gain hands-on experience diagnosing and treating neurological conditions.
Many neurologists also pursue fellowships to specialize further, such as in pediatric neurology, neuro-oncology, or movement disorders.
Skills and Expertise: Neurologists must have excellent analytical and problem-solving skills, as many neurological disorders present with subtle or complex symptoms.
They also need strong communication skills to explain diagnoses and treatment plans to patients and their families.
Types of Neurologists: Neurology has several sub-specialties. Pediatric neurologists treat children with neurological conditions, neuro-oncologists focus on brain and spinal tumors, and movement disorder specialists help patients manage conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
Each type of neurologist combines medical expertise with specialized techniques to improve patient outcomes.
In short, a neurologist is not just a doctor they are experts who dedicate years to understanding the nervous system and improving patients’ quality of life.
Common Conditions Treated by Neurologists
Neurologists treat a wide variety of conditions that affect the nervous system. These disorders can range from mild and manageable to severe and life-changing, making the role of a neurologist essential for maintaining neurological health.
One of the most common issues neurologists see is headaches and migraines. Chronic migraines, tension headaches, and cluster headaches can significantly impact daily life, and neurologists provide diagnosis, preventive strategies, and treatment plans to reduce frequency and intensity.
Another major area is epilepsy and seizure disorders. Neurologists identify the type of seizure, determine its underlying cause, and recommend treatments including medications, lifestyle changes, or surgical options if necessary.
Movement disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and essential tremors, are also commonly treated by neurologists. These specialists help manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve patients’ quality of life.
Neurologists also address neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and other forms of dementia. Early diagnosis and treatment can help slow progression and support cognitive and physical function.
Additionally, neurologists are vital in stroke management, evaluating both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, and guiding rehabilitation to regain lost function.
Other areas include spinal cord injuries, peripheral neuropathy, and nerve disorders, which can cause chronic pain, weakness, or numbness.
By combining advanced diagnostic techniques with personalized treatment plans, neurologists play a key role in restoring function, relieving symptoms, and improving overall quality of life for patients with neurological conditions.
What Tests and Procedures Do Neurologists Perform?
Neurologists rely on a combination of clinical evaluations, diagnostic tests, and specialized procedures to accurately identify and treat neurological disorders.
The first step in most cases is a comprehensive neurological examination, which evaluates reflexes, muscle strength, coordination, balance, sensation, and cognitive function.
This hands-on assessment helps the neurologist detect abnormalities in the nervous system that may indicate underlying conditions.
For more detailed insights, imaging tests are often used. These include MRI scans, CT scans, and sometimes PET scans, which provide high-resolution images of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
These imaging techniques are crucial for diagnosing tumors, strokes, multiple sclerosis, and structural abnormalities.
Electrophysiological tests are another important tool. EEG (electroencephalogram) measures electrical activity in the brain, helping diagnose epilepsy and other seizure disorders.
EMG (electromyography) and nerve conduction studies evaluate muscle and nerve function, assisting in the diagnosis of neuropathies, muscle disorders, or spinal nerve problems.
In some cases, neurologists may also recommend laboratory and genetic tests, including blood tests, cerebrospinal fluid analysis, or genetic screening, to pinpoint causes of neurological symptoms.
These tests can help detect infections, autoimmune disorders, and hereditary neurological conditions.
By combining physical examinations, advanced imaging, and specialized tests, neurologists can create accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
These procedures ensure that patients receive the most effective care for their specific neurological needs.
When Should You See a Neurologist?
Knowing when to see a neurologist is crucial for early detection and effective management of neurological conditions. While many symptoms may seem minor at first, they can sometimes indicate serious underlying issues.
Persistent or severe headaches, sudden changes in vision, frequent dizziness, or unexplained numbness and weakness are common warning signs that warrant a neurological evaluation.
Additionally, recurrent seizures, tremors, or difficulties with movement are clear indicators that consulting a neurologist is necessary.
Stroke symptoms, such as sudden facial drooping, slurred speech, or one-sided weakness, require immediate attention.
In these cases, a neurologist’s expertise is critical to minimize damage and improve recovery outcomes.
Patients with memory problems, confusion, or changes in cognitive function should also seek neurological care, as early intervention can help manage conditions like Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia.
Often, patients are referred to a neurologist by their primary care physician, especially when symptoms are persistent, unexplained, or complex.
High-risk individuals such as those with a family history of neurological disorders or chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension may benefit from routine neurological check-ups even before severe symptoms appear.
Early consultation with a neurologist not only helps identify conditions promptly but also improves long-term outcomes.
By recognizing warning signs, seeking timely care, and following preventive measures, patients can maintain better neurological health and enhance their overall quality of life.
Treatment Approaches Used by Neurologists
Neurologists use a variety of treatment approaches tailored to each patient’s condition, severity, and overall health.
Medications are often the first line of treatment. For example, anti-seizure drugs help manage epilepsy, pain relievers and preventive medications control chronic migraines, and neuroprotective medications slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s or multiple sclerosis.
Correct medication management is crucial for effective symptom control and improved quality of life.
In addition to medications, neurologists often recommend therapies to support recovery and maintain function. Physical therapy improves mobility, strength, and balance, while occupational therapy helps patients perform daily activities more independently.
Speech therapy may be necessary for individuals with communication difficulties due to stroke or neurological conditions. These therapies complement medical treatments and promote long-term rehabilitation.
In some cases, surgical interventions may be required. Neurologists often collaborate with neurosurgeons to determine the need for procedures such as deep brain stimulation for movement disorders or surgery to remove tumors.
Lifestyle modifications are also a key part of neurological care. Neurologists advise on proper diet, regular exercise, stress management, and sleep hygiene to reduce risk factors and improve overall neurological health. Preventive measures, combined with medications and therapy, often result in the most effective outcomes.
By combining medications, therapies, surgical options, and lifestyle strategies, neurologists provide comprehensive care designed to relieve symptoms, slow disease progression, and enhance patients’ overall quality of life.
Differences Between Neurologists and Other Specialists
Many people often confuse neurologists with other medical specialists, but their roles and expertise are distinct. Understanding these differences can help patients seek the right care for their symptoms.
Neurologist vs. Neurosurgeon: While neurologists diagnose and manage neurological disorders using medications, therapies, and lifestyle interventions, neurosurgeons perform surgical procedures to treat brain, spinal cord, or nerve conditions.
For example, a neurologist may treat Parkinson’s disease with medications, while a neurosurgeon might perform deep brain stimulation if surgery is necessary.
Neurologist vs. Psychiatrist: Both neurologists and psychiatrists deal with the brain, but their focus differs. Psychiatrists specialize in mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, or bipolar disorder, and primarily use therapy and psychiatric medications.
Neurologists, on the other hand, focus on physical disorders of the nervous system, like epilepsy, stroke, or multiple sclerosis.
Neurologist vs. Orthopedic or Physical Medicine Specialists: Orthopedic doctors treat musculoskeletal issues such as bone, joint, or spine problems, whereas neurologists focus on nerve-related causes of pain, numbness, or weakness.
Physical medicine specialists may aid in rehabilitation, but neurologists diagnose the underlying neurological causes and create treatment plans.
By understanding these distinctions, patients can make informed decisions about who to consult for specific symptoms.
Choosing the right specialist ensures accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and faster recovery, ultimately improving quality of life.
FAQs:
Many people have questions about neurologists, their role, and the conditions they treat. Addressing these FAQs can help readers understand when and why to consult a neurologist.
1. What does a neurologist do?
A neurologist diagnoses, treats, and manages disorders of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. They handle conditions like epilepsy, migraines, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, strokes, and neuropathies.
2. How long does it take to see results from neurological treatment?
The timeline depends on the condition and treatment approach. Some issues, like migraines or minor nerve disorders, may improve within weeks. Chronic or degenerative conditions, such as Parkinson’s or multiple sclerosis, require ongoing management and may take months to show noticeable improvements.
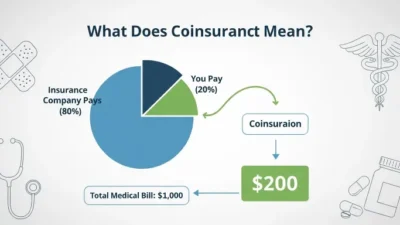
3. Are neurologist visits covered by insurance?
In most cases, health insurance covers neurologist consultations, diagnostic tests, and prescribed treatments. Coverage can vary based on insurance plans, so it’s essential to confirm with your provider before scheduling a visit.
4. Can neurologists perform surgeries?
Generally, neurologists do not perform surgery; that is the role of neurosurgeons. However, neurologists may collaborate with neurosurgeons when surgical interventions are necessary and provide post-operative care.
5. When should I see a neurologist?
Consult a neurologist if you experience persistent headaches, seizures, dizziness, numbness, weakness, memory issues, or unexplained movement problems. Early diagnosis often improves treatment outcomes and quality of life.
Answering these common questions helps patients make informed decisions and understand the importance of neurological care.
Conclusion:
Neurologists play a vital role in maintaining the health of the nervous system, which includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
Their expertise allows them to diagnose, treat, and manage a wide range of neurological conditions, from common issues like migraines and dizziness to serious disorders such as epilepsy, stroke, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
By combining specialized knowledge with advanced diagnostic tests, medications, therapies, and lifestyle recommendations, neurologists help patients improve their quality of life and prevent complications.
Understanding when to consult a neurologist is equally important. Persistent headaches, seizures, numbness, weakness, memory problems, or sudden changes in movement or coordination are all signs that professional evaluation is needed.
Early detection and timely treatment can make a significant difference in patient outcomes, especially for progressive or chronic conditions.
Neurologists are distinct from other specialists, such as psychiatrists, neurosurgeons, or orthopedic doctors, because they focus specifically on the functioning of the nervous system.
This specialized approach ensures that patients receive accurate diagnoses and targeted treatments tailored to their unique needs.
In summary, a neurologist is not just a doctor they are highly trained specialists dedicated to understanding and caring for the complex nervous system.
Consulting a neurologist at the right time, following treatment plans, and adopting preventive measures can significantly enhance neurological health.
If you or a loved one experience any concerning neurological symptoms, seeking expert care promptly is essential for long-term well-being.

I am Stephen King, a name that rules both horror legends and humor headlines on Jokestide.com.
I am here to twist words, spark laughs, and turn iconic fame into joke-worthy fun.
I am not the horror I’m the punchline that keeps readers hooked.